Most Long-lived Empires in History

There have been many empires in history, but only a select few have managed to stand the test of time. In this blog post, we will take a look at some of the most long-lived empires in history. These empires have withstood the test of time and conquered vast territories. Let's take a look at some of these impressive empires!
Kanem Empire
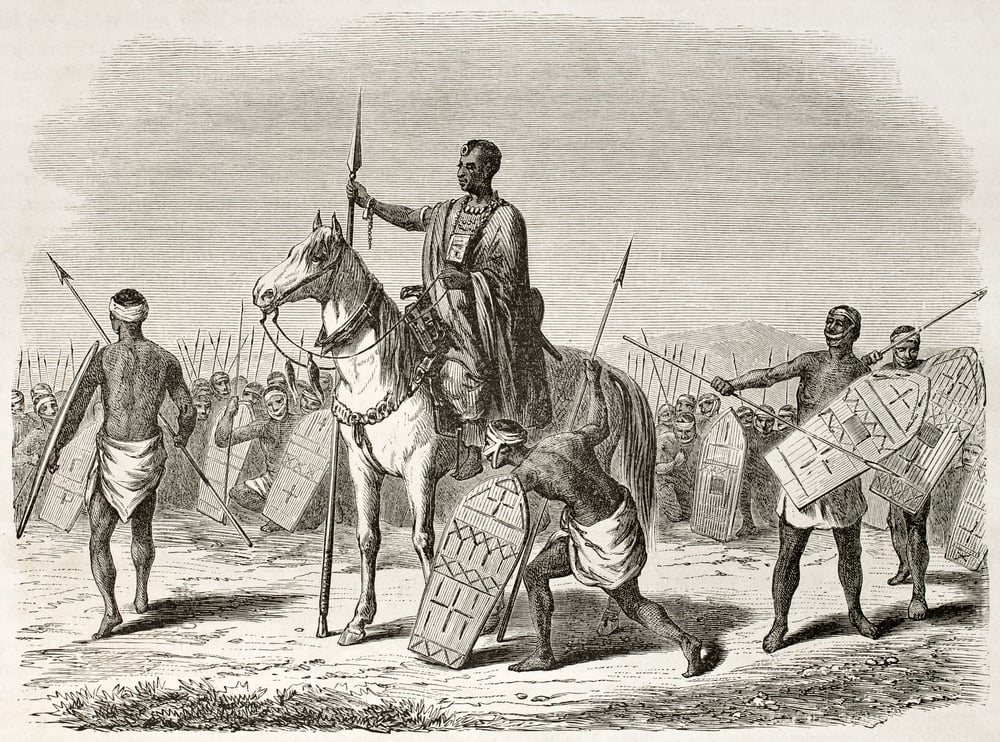

The empire was founded in the 9th century by the nomadic Kanembu people, who inhabited an area in what is now northeastern Niger. Over the next centuries, the Kanembu expanded their control over a large swath of territory in West Africa. At its peak in the 13th century, the Kanem Empire extended from Lake Chad in the north to the Atlantic coast in the south. The empire eventually came to an end in the late 14th century, but its legacy lasted for centuries afterwards. The Kanem Empire was notable for its political stability and its tolerant attitude towards religious and ethnic minorities. It was also one of the few empires in world history that maintained friendly relations with both Europe and Asia. As a result of these factors, the Kanem Empire left a lasting impression on the cultures of West Africa.
Holy Roman Empire

The Holy Roman Empire was a European political power that lasted for centuries. The first iteration of the empire was founded in 800 AD by Charlemagne, King of the Franks. Over the next few hundred years, the empire would see various changes in leadership and territory. However, it would remain a powerful force in European politics until its dissolution in 1806. During its time, the Holy Roman Empire was one of the most influential and important empires in the world. It played a significant role in shaping the course of European history. For example, the empire was a key player in the Crusades, as well as the Reformation. Additionally, its large size and central location made it a major economic power. The Holy Roman Empire was truly one of the most long-lived empires in history.
Silla Empire
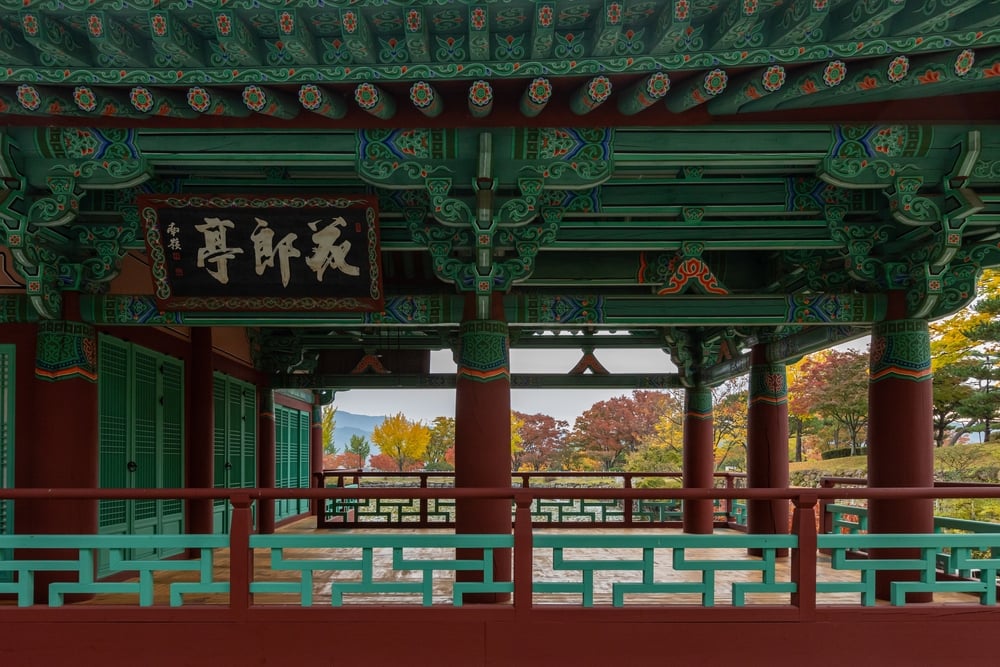

The Silla Empire was one of the most long-lived empires in history, lasting from 57 BC to 935 AD. This ancient empire was located in what is now southeastern Korea, and at its peak it controlled nearly two-thirds of the Korean Peninsula. The Silla dynasty was characterized by a strong central government, a thriving economy, and a rich culture. It was also a period of great military expansion, as the Silla armies conquered the neighboring kingdoms of Baekje and Goguryeo. The Silla Empire ultimately fell due to internal strife and invasions by the Mongol Empire, but its legacy continues to be felt in present-day Korea.
Republic of Venice
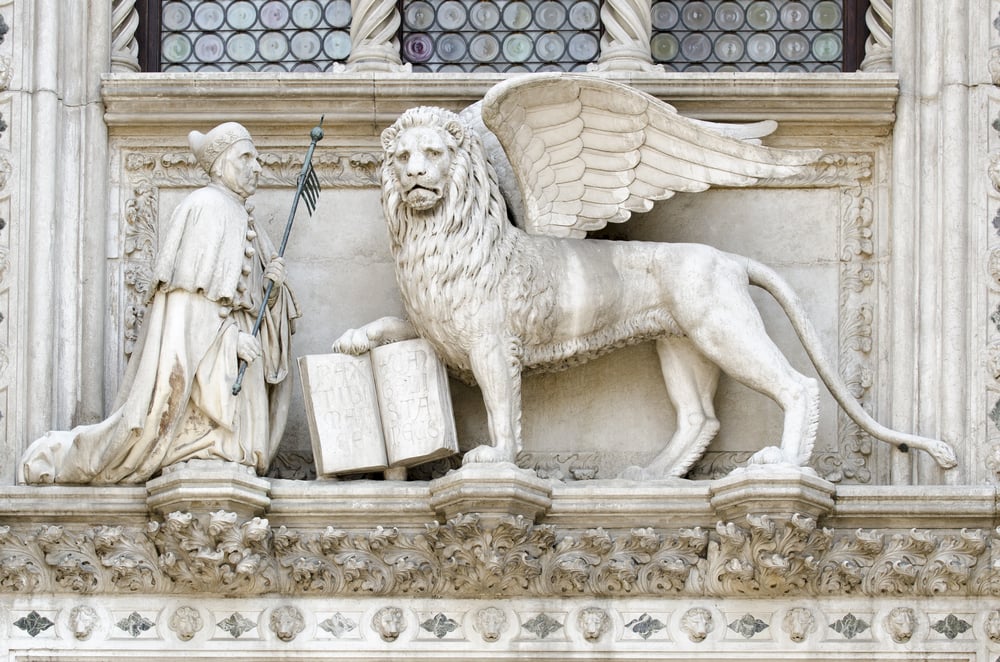

For over a thousand years, Republic of Venice thrived on the strength of its navy and its commerce, controlling a vast empire that stretched from the Mediterranean to the Black Sea. The Venetian Republic was a model of stability in an age of civil unrest, and it was able to weather the storms of war and revolution with surprising resilience. Even today, the city of Venice is a testament to the longevity of the Venetian Empire, with its grand palaces and beautifully preserved churches testifying to a proud and prosperous past. The Republic of Venice may be gone, but its legacy endures.
Kush Empire
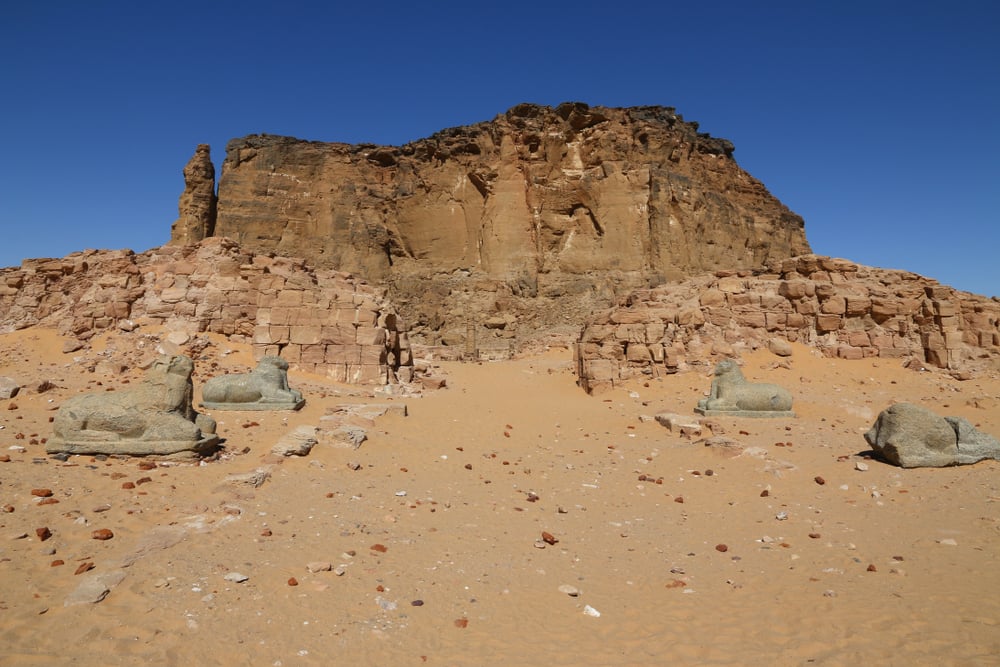

The Kush Empire was one of the most long-lived empires of ancient times. Spanning over a thousand years, from circa 1050 BCE to 350 CE, the Kushites ruled over a territory that extended from present-day Sudan to Egypt. During this period, they created a distinctive culture that was influential far beyond their own borders. Among the most notable achievements of the Kushites were their mastery of iron-working and their construction of monumental architecture, such as the temple complex at Jebel Barkal. In more recent times, the Kushites have been the subject of intense scholarly scrutiny, providing new insights into the history and culture of this fascinating civilization.
Roman/Eastern Roman Empire
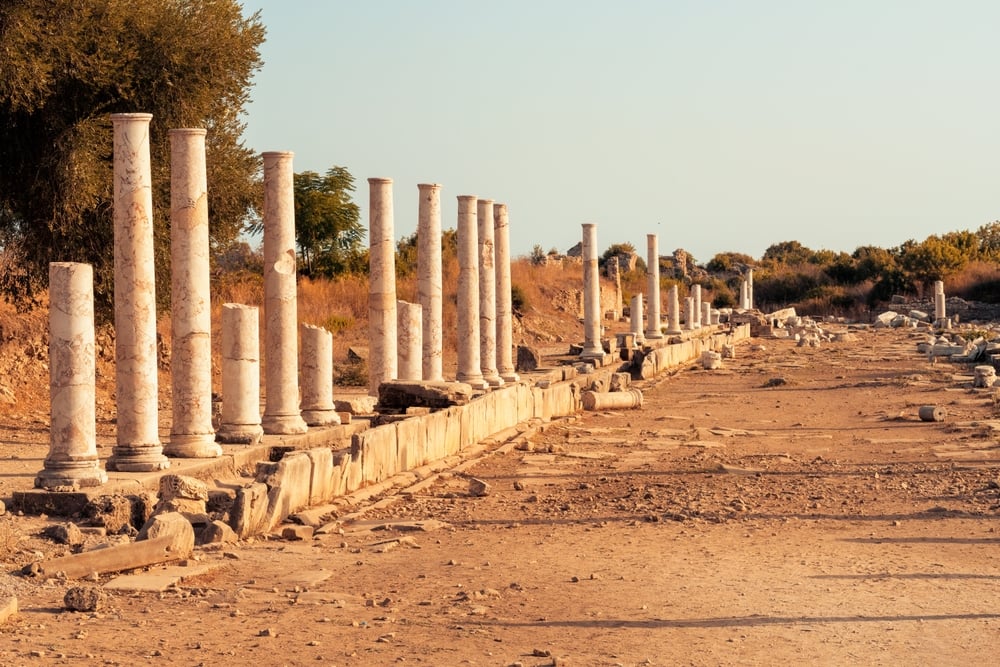

The Roman Empire was one of the most long-lived empires in history. It was founded in 753 BCE, and continued to exist in some form until 1453 CE. During that time, the empire changed drastically in both size and nature. At its peak, the Roman Empire controlled a territory that extended from Britain to North Africa and from Spain to the Middle East. However, over time the empire began to fragment, and by the end of the 5th century CE it had split into two separate entities: the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. Nevertheless, both empires continued to exist for centuries afterwards. The Eastern Roman Empire survived until 1453 CE, while the Western Roman Empire lingered on until 476 CE. As such, the Roman Empire can rightfully be seen as one of the most enduring empires in history.