Everyone's on the Hunt for the Element Lithium

Do you know what element is the most sought-after on the planet? Lithium! That's right, this soft metal has become one of the world's most precious resources. Everyone is looking for a way to get their hands on it, and it's no wonder why. Lithium is essential in the production of batteries, and with the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy, demand for lithium is only going to increase. So what can you do to get your share of this valuable resource? Read on to find out!
Lithium Characteristics
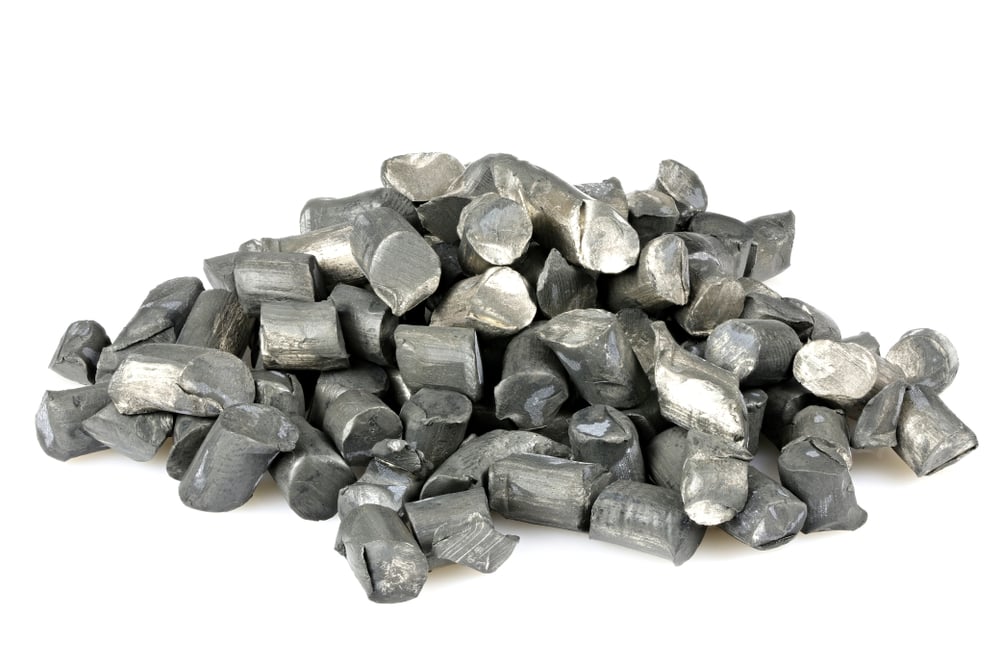

Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that is part of the alkali metal group. It is the lightest metal and has the lowest density of all the elements. Lithium is highly reactive and flammable. It does not occur naturally in its elemental form, but can be found in some minerals, such as spodumene and lepidolite. Lithium is used in a variety of products, including batteries, alloy steels, pharmaceuticals, and glass ceramics. When lithium reacts with water, it forms lithium hydroxide, which is used as a caustic agent and corrosion inhibitor. Lithium carbonate is used to treat bipolar disorder and other mental health conditions. Lithium chloride is used as a dehumidifying agent.
Lithium Soda, Batteries and Mood Stabilizers

You may not know this, but the lithium in your mood stabilizers and batteries has a long and often surprising history. In the early 19th century, lithium was first isolated by Swedish chemist Johan August Arfwedson during an analysis of petalite, a mineral whose name comes from the Greek word for "rock". It wasn't until 1855 that English chemist Sir Humphry Davy realized that lithium could be used as an element. In fact, Davy was so impressed by its potential that he nicknamed it "lithos", meaning "stone" in Greek. By the end of the 19th century, lithium had been used to create everything from cocktail stirrers to photographic film. But it wasn't until 1949 that researchers began to explore its potential as a treatment for mental illness. Since then, lithium has been used as a mood stabilizer for people with bipolar disorder and other conditions. Today, it remains an important part of many people's lives.
The Lithium Triangle
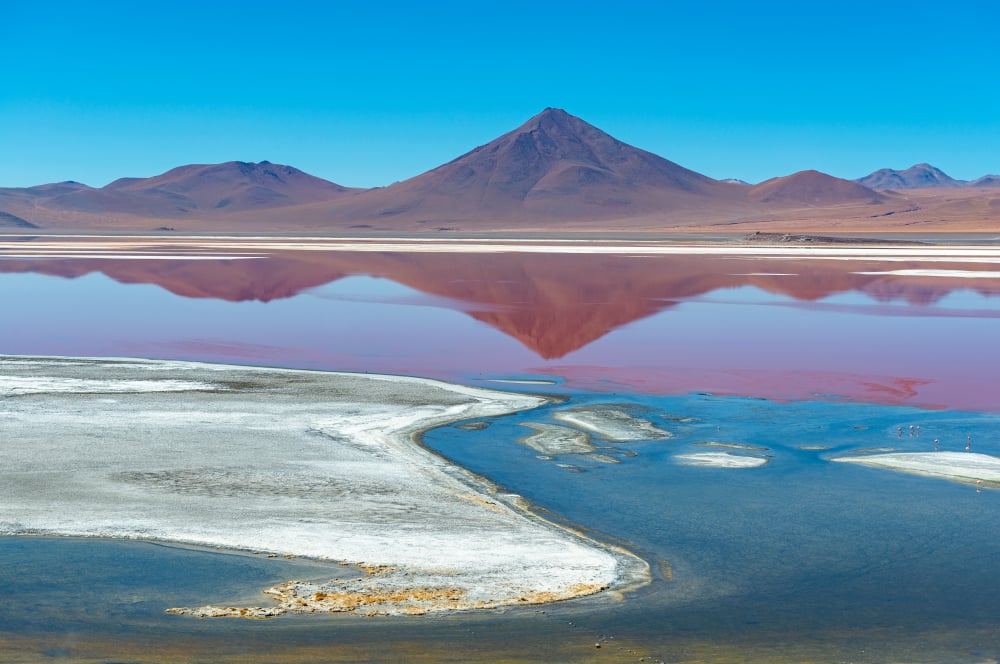

The Lithium Triangle is a region in South America that is home to some of the world's largest reserves of lithium. The triangle is located in the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile. These three countries have been working together to develop their lithium resources and create a sustainable industry. In 2016, they signed an agreement to create a joint venture called LiCoBol, which will manage the production and sale of lithium carbonate. The Lithium Triangle has the potential to become the world's leading supplier of this valuable resource. So far, it has been very successful in meeting global demand for lithium.
Is Lithium Dangerous?

Studies have shown that high levels of lithium exposure can cause neurological damage, thyroid problems, and kidney damage. In addition, lithium has been linked to an increased risk of suicide and self-harm. As a result, some experts believe that lithium should be regulated more closely. However, others argue that the benefits of using lithium far outweigh the risks. Until more research is conducted, the debate over the safety of lithium will continue.
How is Lithium Mined?
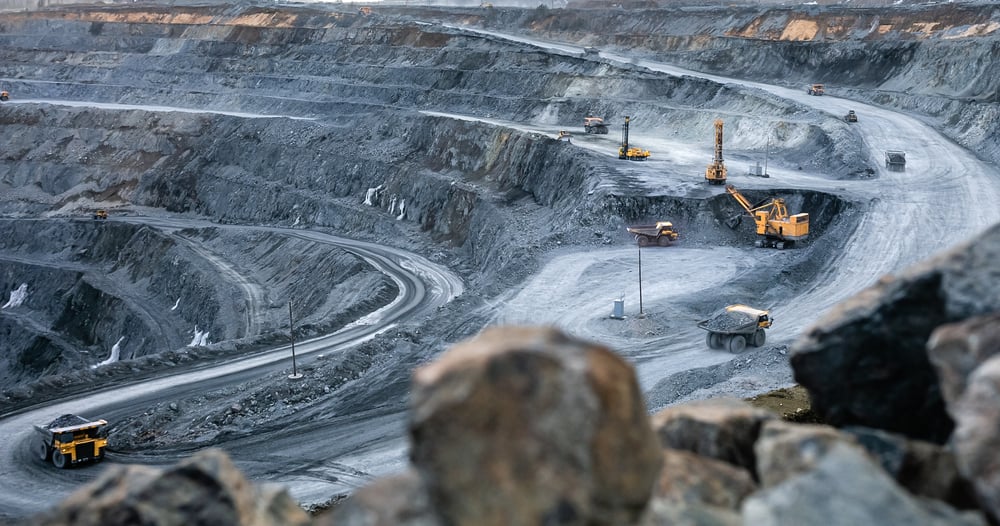

Lithium is typically mined from brine deposits or hard rock minerals. Brine mining is the more common method, as it is simpler and less expensive. Lithium-rich brine is pumped from underground wells and evaporated to concentrate the lithium. This process can take up to 18 months. Hard rock mining is a more complex process that involves extracting lithium from pegmatite and spodumene deposits. First, the ore must be crushed and roasted to release the lithium. Then, it is purified using acid leaching or solvent extraction. This process can take up to two years.
Demand for lithium is expected to continue to rise in the coming years. This is due to the increasing use of electric vehicles and renewable energy, which require batteries that contain lithium. In addition, the use of lithium-ion batteries in laptops, cell phones, and other devices is also expected to increase. As a result, many companies are searching for new ways to mine and process lithium. In fact, some companies are even looking into extracting lithium from seawater! With so much interest in this element, it's clear that the hunt for lithium is only going to intensify in the future. So make sure you get your share while you can!